Spectroscopy is the study of objects based on the spectrum of color they emit, absorb or reflect. Spectroscopy is an important investigative tool in astronomy, where scientists use it to analyze the properties of distant objects. Typically, astronomical spectroscopy uses high-dispersion diffraction gratings to observe spectra at very high spectral resolutions. Helium was first detected by analysis of the spectrum of the sun. Chemical elements can be detected in astronomical objects by emission lines and absorption lines.
The shifting of spectral lines can be used to measure the Doppler shift (red shift or blue shift) of distant objects.
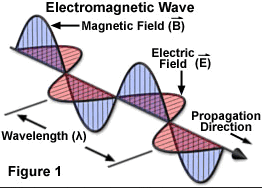
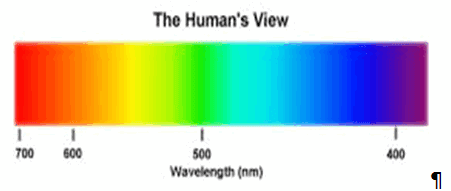
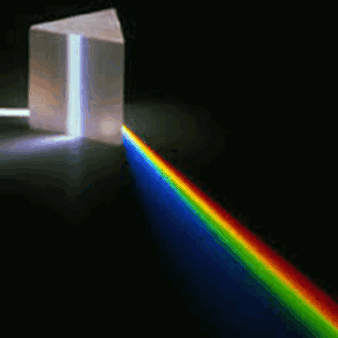
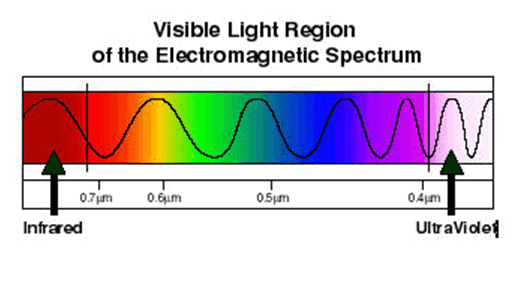
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative energy as a function of its wavelength or frequency. Spectroscopic data is often represented by a spectrum, a plot of the response of interest as a function of wavelength or frequency.
The shifting of spectral lines can be used to measure the Doppler shift (red shift or blue shift) of distant objects.
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative energy as a function of its wavelength or frequency. Spectroscopic data is often represented by a spectrum, a plot of the response of interest as a function of wavelength or frequency.













0 comments:
Post a Comment